|
|
| Lingual braces | Invisalign | Clear Aligner | Metal braces | Clear braces |
Damon braces |
Clarity braces |
Orthognathic Surgery |
|
ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY Bangkok, Thailand |
|
language |
l | THAI |
Under what circumstances would I need orthognathic surgery?
Can these conditions be effectively treated?
At what age is the treatment most effective?
What is involved in the treatment itself?
Before and After treatment
The conditions which
require orthognathic surgery are often refered to as “bad
bites”. There are many types of “bad bites”, with some
having a greater effect on facial esthetics than others. The
common maxillofacial deformities and their clinical
appearances are the following:
1. Protruded Maxilla (upper jaw) :
The upper jaw is protruded beyond the normal limits along with the
teeth. The person cannot close his lips (lip incompetence)
without effort. The teeth are always visible and in most
cases the whole of the gums are visible on smiling (gummy
smile). A gummy smile is mainly due to the vertical excess
of the maxilla.
2. Retruded Maxilla :
This deformity is due to under development of the upper jaw
mainly seen in people who have cleft lip or palate. After
the surgical correction of the cleft lip or palate at a
young age the growth of the maxilla is retarded along with
displacement or destruction of the tooth bud. This causes a
dish shaped face with a hooked or flaring nose and
irregularly aligned, rotated or missing teeth.
3. Protruded Mandible (lower jaw) :
In some people there will be extra growth of the lower jaw
resulting in long jaw. Their faces are very long with
protrusion of the lower teeth and thick lips. Normally on
biting the lower teeth will be inside the upper teeth while
in people with long jaws usually the lower teeth will be
outside the upper arch.
4. Retruded Mandible :
In some people due to developmental deformity or due to
hereditary factors the lower jaw is very small resulting in
a “bird face”. There is no proper development of the chin.
5. Facial Asymmetry :
Sometimes a part of the face maybe overdeveloped or
underdeveloped causing one part of the face to be small or
large. One side of the face is not in symmetry with the
other side giving an unaesthetic appearance.
6. Akylosis of Tempromandibular Joint (TMJ) :
Injury during birth or trauma or infection at a young age
to the tempromandibular joint will result in restricted
mouth opening and reduced growth of the mandible.
7. Nasal Deformity :
Nasal deformities are often seen along with deformities of
the jaw. Some common deformities of the nose are: deviated
nasal septum, flared or constricted ala of the nose, saddle
nose, hooked nose, asymmetrical nose, etc.
These conditions may cause many functional and psychological problems. The good news is that they need not be permanent. Improvement, and often correction, can be attained with the proper procedure. It is a cosmetic surgery and the surgeon envisages changing the face of a person from distortion to proportion. The results of orthognathic surgery can have a dramatic and positive affect on many aspects of your life.
The ideal age for Orthognathic Surgery is after the growth period has been completed (18 years for girls and 20 years for boys), although there are a few exceptions. If the patient has psychological problems due to the deformity of the face then orthognathic surgery may take place at an earlier age.
These conditions may cause many functional and psychological
problems. The good news is that they need not be permanent.
Improvement, and often correction, can be attained with the
proper procedure. It is a cosmetic surgery and the surgeon
envisages changing the face of a person from distortion to
proportion. The results of orthognathic surgery can have a
dramatic and positive affect on many aspects of your life.
Evaluation :
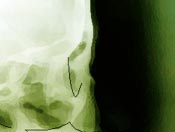
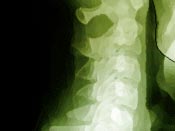
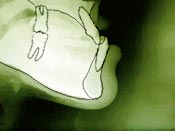
After the initial examination a thorough examination with
facial measurements, photographs, x-rays, and dental
impressions will be carried out. A complete medical
examination will follow. This rules out any health problems
that would interfere with the surgery or the administration
of General Anesthesia.
Pre-surgical Orthodontia :
The Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon and the Orthodontist will
work closely together during your treatment. Orthodontic
treatment (braces) is started before surgery. The teeth are
moved and repositioned into proper alignment before surgery
if necessary.
Preparing for Surgery :
The Orthognathic Surgery will take place in a hospital under
general anesthesia. You will be admitted to the hospital one
day prior to surgery and will be advised on dietary
conditions for the days leading up to surgery. You will
probably be required to stay in the hospital for a week or
so until you have recovered from the surgery. You may need
blood transfusion during the surgery. You will then undergo
a full medical checkup. You should as always, maintain a
good standard of oral hygiene before and after surgery.
Surgical Procedures :
Orthognathic Surgery lasts anywhere from
1½ hours to several hours depending on the type of surgery
needed. Incisions are made inside the mouth during surgery
and there will be no visible external scars. However if
external incision has to be made, as in surgeries of the
tempromandibular joint , care is taken to conceal it in the
natural skin creases or folds. Meticulous suturing technique
can reduce the scar formation.
HOME
l SERVICE
l DENTISTS
l TECHNOLOGY
l FACILITIES
l ABOUT US
l SITE MAP
PROMOTION
l PRICE&DURATION
l CONSULTATION
l FAQ
l LINKS
l MAP
l TESTIMONIALS
l OUR LAB
AIR-FLOW
l DENTAL LASER SYSTEM
l ENDODONTIC EQUIPMENT
l DENTAL UNITS
l OPERATING LAMP
l WHITENING SYSTEM
DENTAL MICROSCOPES
l NOBEL GUIDE
l STERILIZATION ROOM
l X-RAY
l ELECTROSURGICAL SYSTEM
l MINIPIEZON
...............................................................................................................................................
MAKE SURE OF YOUR SMILE. Copyright© 2004 SILOM DENTAL BUILDING. All Rights Reserved.
Local Call : 0 2636 9092-5,
International Call : (+) 66 2636 9091, (+) 66 2636 9097
e-mail :
silomdental@silomdental.com